Data Science is a new and evolving professional field. As a result, the terms ‘Data Scientist’ and ‘Data Analyst’ are sometimes used for the same job description, based on the company providing the opportunity. Generally, the job responsibilities of a Data Scientist tend to pay attention to future-oriented data modeling with the focus on predicting future trends, while the job of a Data Analyst is on looking at data to unveil current patterns. Professionals use similar analytical tools in both roles. I have seen many people still searching for How To Become a Data Scientist. So, I thought to write a detailed guide to become a data scientist.
 Role of Data Scientist – How To Become a Data Scientist
Role of Data Scientist – How To Become a Data Scientist
A data scientist uses statistical methods, such as mixed modeling, predictive response modeling, sales response modeling, experimental design, CART/CHAID, latent class segmentation, cross-sectional and time series analysis, discrete choice modeling, data mining, and optimization techniques to cater to client business requirements. Professionals in this role also participate with internal consulting teams to keep up analytic objectives, work plans, and approach and offer programming and analytic help to internal consulting or related teams, writing macros while automating statistical procedures using SAS and Microsoft Office; perform analytics using SAS; interpret analytical model results to turn them into business insights for the client.
Role of Data Analyst
The role of data analysts requires them to fulfill the following requirements:
- Use leading-edge tools to extract and evaluate customer and transactional data
- Understanding loyalty programs and marketing campaign impact on customer behavior
- Develop actionable customer segments and clusters for reporting and targeting purposes
- Evaluate email campaign data to recommend and improve promotional opportunities
- Implement new analytical methodologies to provide useful insights to clients
- Present and describe results to both internal and external customers
Skills Needed to Become a Data Scientist
Data scientists are called big data wranglers. They take large amounts of messy data points, whether unstructured or structured, and refine and arrange them with their formidable capabilities in math, statistics, and programming. They then implement all their analytics powers to unlock hidden solutions to business challenges and implement them for the business. In other words, Data scientists use their knowledge and skills in statistics and modeling to turn data into actionable insights about everything from the development of the product to customer retention to developing new business opportunities.
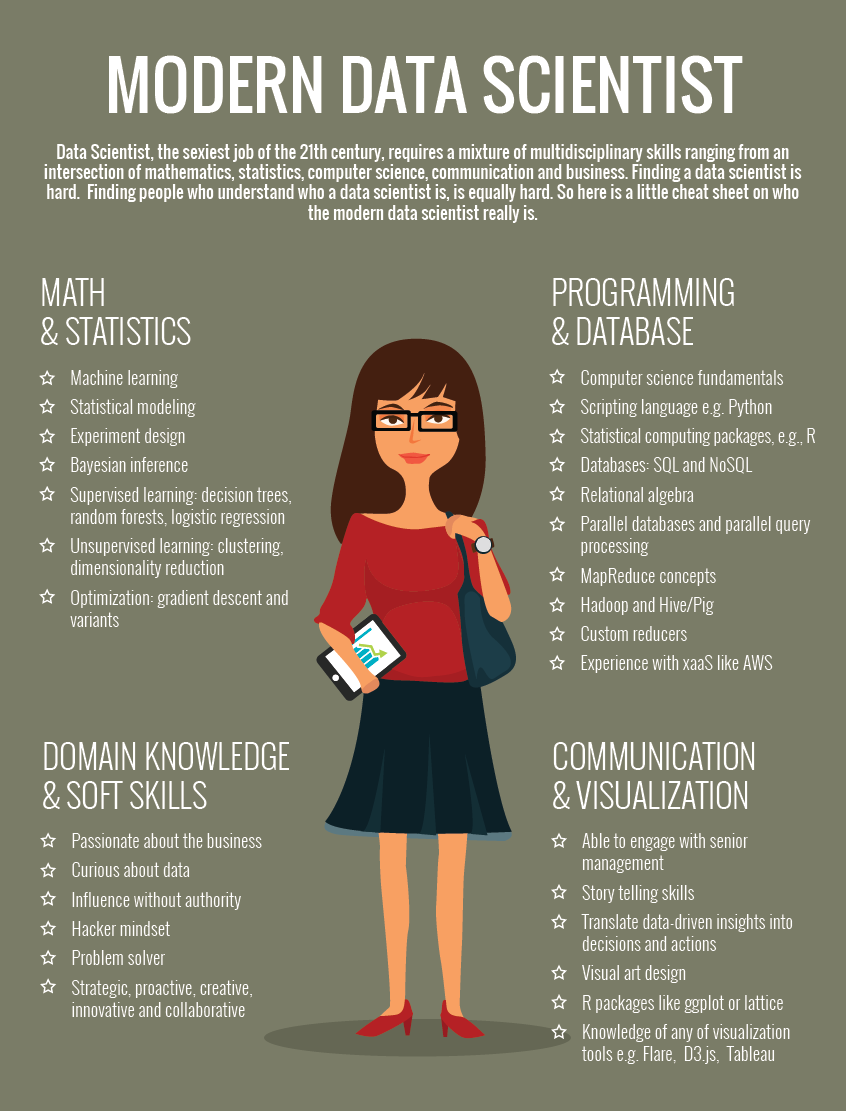 You need to have both technical and non-technical skills to perform a data scientist’s job in the right way. Technical skills evolve at three stages of Data Science.
You need to have both technical and non-technical skills to perform a data scientist’s job in the right way. Technical skills evolve at three stages of Data Science.
They include:
- Data Capture & pre-processing
- Data Analysis & pattern recognition
- Presentation & visualization
To perform three stages, three sets of tools are required – tools for pulling data, tools for evaluating the data, and tools for presenting the results.
Here are the various tools available to perform the same:
1. Tools for data pulling & pre-processing
a. SQL
This is an important tool for most data scientists, irrespective of data types- structured or unstructured data. Most companies use the latest SQL engines like Apache Hive, Impala, Spark-SQL, Flink-SQL, etc.
b. Big Data Technologies
This is one of the necessary skills important to becoming a Data Scientist. A data scientist must have a deep understanding of different big data technologies – 1st Gen technologies, for instance, Apache Hadoop & its ecosystem (hive, pig, flume, etc). You can even enroll in a Big Data Hadoop training to understand the workings of the Hadoop architecture. Data scientists should also understand NextGen tools like – Apache Spark and Apache Flink (Apache Flink is likely to replace Apache Spark quickly because Flink is a general-purpose Big data engine, which can manage real-time stream efficiently).
c. UNIX
UNIX or Linux server stores most raw data before putting it in a data-store, so there is no need to depend on a database to access the raw data. Therefore, it is important for data scientists to have an in-depth understanding of Unix knowledge.
d. Python
Python is a popular language for the data scientist. Python is an interpreted and object-oriented programming language that has dynamic semantics. It is a high-level language with active binding and typing.
2. Tools for Data Analysis & pattern matching
This depends on your statistical knowledge level. Some tools are used to perform advanced statistics, and some are used for basic statistics.
a. SAS
Most companies use SAS, so you need to have a basic SAS understanding. It is a software suite that mines, alters, controls, and retrieves data from different sources and performs statistical analysis on it. SAS offers a graphical point-and-click user interface to all non-technical users and highly advanced options with the help of the SAS language. It will help you manipulate equations.
b. R
R is widely known in the statistical world. It is an open-source tool and language that is entirely object-oriented so that you can use it anywhere. I use R to implement the most important things, so this is a vital tool for any data scientist to know.
c. Machine Learning
Machine learning is the most useful and most demanding tool data scientists need to have. Machine learning algorithms are used to perform advanced data analytics, predictive analytics, and advanced pattern matching. There are many machine learning tools available in the market, such as weka, nltk, etc. In fact, machine learning tools are at the top of the list of big data technologies that grab industry attention, such as Mahout (on top of Hadoop), MLlib (on top of Spark), FlinkML (on top of Flink).
3. Tools for Visualization
a. Tableau
It is in great demand by data scientists across the globe. Tableau bridges the gap between data scientists and lay-people and helps business data reach people in charge, so they can use it to make informed decisions.
Its users can develop and distribute an interactive and shareable dashboard, which explains the trends, variations, and volume of the data in the form of graphs and charts. Tableau is easy to connect to files, relational, and Big Data sources to access and process data. The software allows real-time collaboration and data blending which makes it very highly innovative. If you are new to Tableau, you can check our Online Tableau Training for more details.
b. JMP (SAS subsidiary)
It is a data analysis tool used by hundreds of scientists, engineers, and other data explorers across the world. Its users leverage robust statistical and analytical capabilities in JMP to develop new insights.
c. R
R has great visualization support, like ggplot2, lattice, rCharts, google charts, shiny for web apps for presentations, etc.
It offers
- efficient data handling and high storage facilities,
- a suite of operators to calculate on arrays, in typical matrices,
- a large, integrated, and coherent collection of intermediate tools for data analysis,
- graphical facilities to evaluate data and display either on-screen or in hardcopy, and
- a developed, easy, and effective programming language which involves conditionals, loops, input and output facilities, and user-defined recursive functions.
- Apart from the previously mentioned tools, the following tools are also popular – JasperSoft, SAP BI, QlikView, MicroStrategy, etc.
4. Non-Technical Skills
a. Business Acumen
One needs to have a complete understanding of the industry he/she is working in to know the problems faced by the organization. A data scientist needs to find out which issues are critical and which aren’t and find new ways to leverage data.
b. Communication Skills
Companies look for data scientists who can confidently and precisely translate their insights on data to other members. A data scientist empowers them with quantified insights.
c. Analytical Problem-Solving
Analytical problem-solving skills are a great demand for Data Scientist so the right approach can become a reason for maximum output in available time and assets.
3. Various Certifications for Data Scientist
Once you have mastered the above skills required to be a Data Scientist, you can go for a Data Scientist certification. Here are a few Data Scientist certifications you can focus on:
a. Cloudera Certified Professional: Data Scientist (CCP: DS)
CCP: DS objective is to indicate advanced skills in working with big data. It includes three exams – Descriptive and Inferential Statistics, Unsupervised Machine Learning, and Supervised Machine Learning – and professionals must show their skills by developing and implementing a production-ready data science solution under real-world conditions. You can also go through data science training in hyderabad for deep understanding.
b. Certified Analytics Professional (CAP)
This certification came in 2013 by the Institute for Operations Research and the Management Sciences (INFORMS) and target data scientists. Aspiring candidates have to demonstrate their expertise in the end-to-end analytics process. This certification encompasses the framing of business and analytics problems, data and methodology, model building, deployment, and lifecycle management.
c. EMC: Data Science Associate (EMCDSA)
The EMCDSA certification checks the ability to implement common techniques and tools needed for big data analytics. Candidates would be tested on their technical expertise in tools like “R”, Hadoop, and Postgres, etc. and their predictive acumen.
It is easy to believe that becoming a data scientist is a hard path to take up. However, this isn’t true. With preparation and persistence, a data scientist’s profession is easy to undertake and excel in. This is an exciting field to be in, and professionals in this field are often well rewarded.
Now that you know how to become a data scientist, let’s have a quick look at what data scientists usually do in their day-to-day work.





[…] and you’ll find Godaddy advertisement there. Seems they have invested a lot on data and using data analysis to optimize their […]
thanks for sharing nice information and nice article and very useful information…..